River erosion – creating force in the rivers

River erosion sculpts Earth’s surface, carving valleys, carrying sediment, and meandering across plains as water’s energy reshapes the land over time.
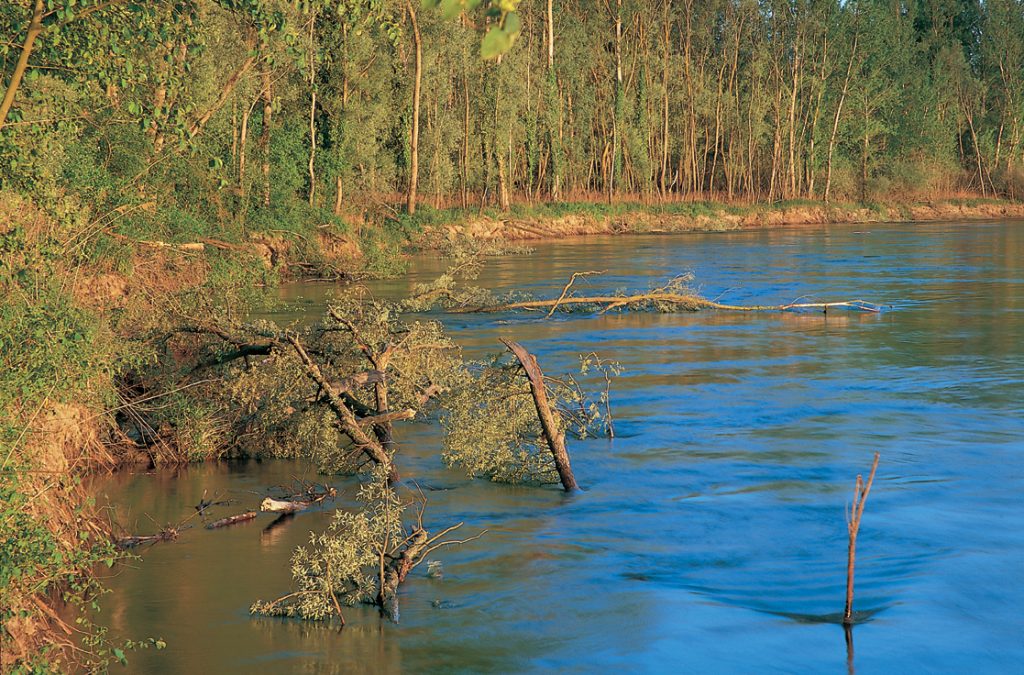
The image below captures the raw power of river erosion. Trees that stood tall on the bank just days ago now lie toppled in the water, their leaves still vividly green. It may look like an apocalyptic scene—but in nature, destruction is often just the beginning of rebirth.

How?
River erosion is a natural process occurring in nearly every river. However, human activities can accelerate it—such as waves triggered by sudden dam releases. At some dams, this occurs daily in a rhythmic pattern known as hydropeaking, intensifying the river’s erosive force.
The Power of Water: How Rivers Shape the Earth
River erosion is one of the most powerful forces sculpting the surface of the Earth. The immense energy of flowing water destabilizes riverbeds, carving valleys deeper and wider over long periods. As rivers cut through the landscape, they carry away sediment delivered to their floors by mass wasting. In the plains, rivers erode the sediment and meander gracefully across wide floodplains, constantly reshaping the land.
Water possesses energy, driven by the force of gravity, which is partly expended on the riverbed. The greater the energy, the stronger the erosion. While the erosion of riverbanks is often most visible, it also relentlessly wears away the river bottom.
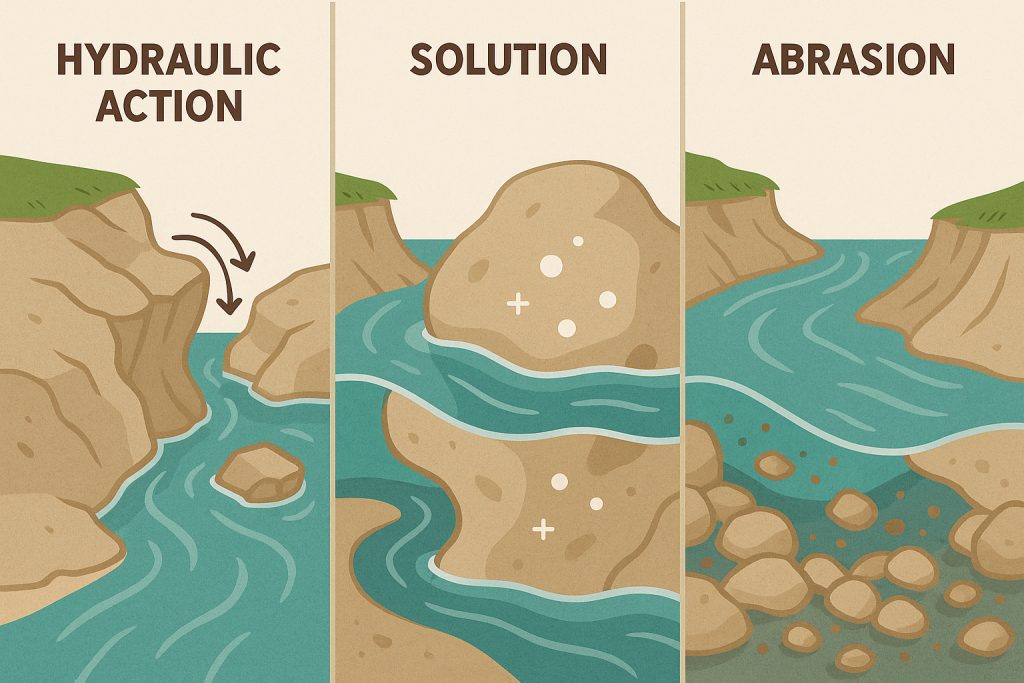
Streams erode rock and sediment through three primary processes—hydraulic action, solution, and abrasion:
-
Hydraulic action is the ability of flowing water to pick up and move rock and sediment. The force of rushing water swirling into a crevice can crack and dislodge fragments, carrying them downstream. Hydraulic force also erodes loose materials from stream banks, especially along the outside of curves.
-
Solution is a slower yet effective form of erosion, where water chemically dissolves rock. Limestone is especially vulnerable, and even sandstone can be affected when water dissolves the calcite cement, freeing individual grains for transport.
-
Abrasion is the grinding down of the stream channel by the friction and impact of the river’s sediment load, mostly sand and gravel. This process is especially potent along rocky streambeds, where the sediment acts like sandpaper, slowly carving and deepening the channel.
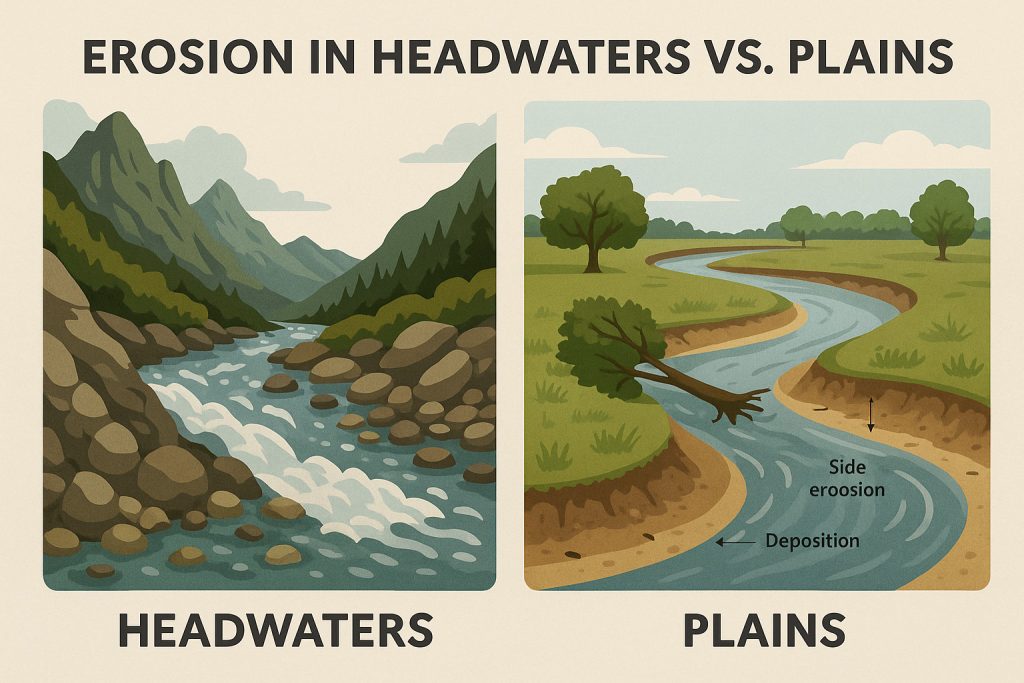
Headwaters: Where River Erosion Begins
River erosion often begins right at the source—typically high in the mountains, where the terrain is steep and the river flows fast, brimming with rapids and energy. In these upper reaches, the river aggressively cuts into large rocks, breaking them down into loose sediment.
Headwaters of the river
This sediment, varying in size from boulders to cobbles, gravel, sand, and silt, travels downstream. The heaviest particles roll or bounce along the riverbed, while finer materials like sand and silt are carried in the water column as suspended load.
Hard rocks of the canyon prevent side erosion.
In these mountainous zones, lateral (side) erosion is usually minimal. The bedrock is often very hard, preventing the river from shifting sideways. Instead, the erosion is primarily vertical, carving deep valleys and canyons that remain narrow and anchored over time.
Shaping the Plains: River Erosion in Lowlands
Downstream, the river begins to flow through much softer alluvial plains (floodplains), composed mostly of sediment deposited over millennia. Here, side (lateral) erosion becomes much more pronounced, as seen in the first image. The riverbanks are constantly eroded, not just by the flow of water, but also by weathering from both air and moisture.
Freshly eroded river bank made of gravel and sand
This erosion intensifies during seasonal floods—a completely natural process—when the river carries significantly more energy than under normal conditions. As a result, the river begins to shift laterally, forming meanders that twist and curve across the landscape.
Strong river erosion in the alluvial floodplain, the situation after the flood
Importantly, erosion is not just about the river taking away land. If that were the case, rivers would eventually become kilometers wide—but they don’t. That’s because erosion is balanced by deposition: while one bank is worn away, the river deposits sediment on the opposite side, maintaining its channel while still reshaping the landscape.
When Erosion Becomes a Problem: Human Impacts and River Regulation
While river erosion plays a vital role in shaping natural landscapes, it can become highly destructive when human settlements are built too close to the riverbanks. Floods and lateral erosion can undermine buildings, roads, bridges, and farmland, leading to significant economic losses and safety hazards.
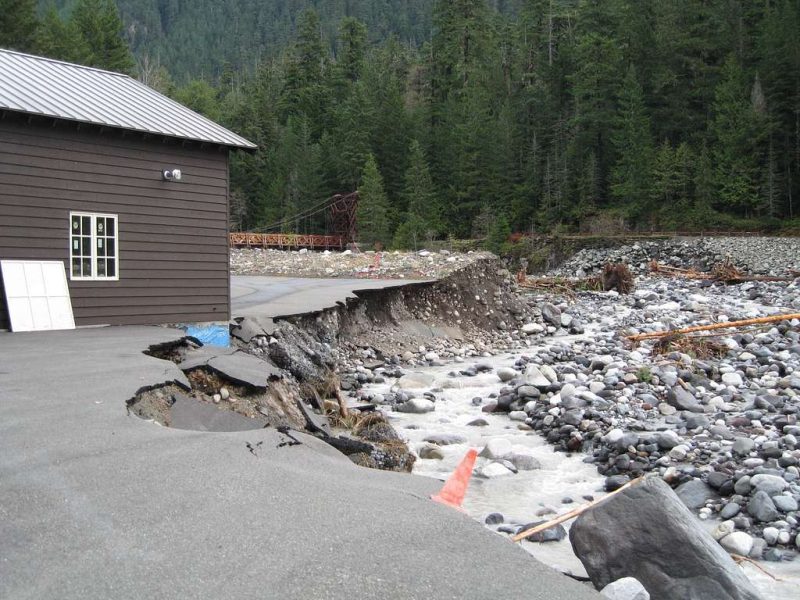

To protect infrastructure, people often resort to river regulation—constructing embankments, levees, ripraps, culverts, and other forms of artificial bank protection. These structures are designed to prevent the river from moving laterally and to contain floods within a fixed channel.
However, restricting a river’s natural movement comes with a cost.
When the river is no longer allowed to erode sideways, its kinetic energy must be spent elsewhere. As a result, the river often begins to erode its own bed, leading to a process called riverbed incision. This can cause the river channel to deepen unnaturally, creating riverbed instability and degradation.
Over time, this not only damages aquatic habitats but can also weaken the very flood defenses meant to protect human infrastructure. In extreme cases, the river may become disconnected from its floodplain, reducing its natural capacity to store floodwater and further increasing flood risks downstream.
Erosion and Biodiversity: Nature’s Creative Force
While river erosion can pose risks to human infrastructure—especially if buildings or roads are placed too close to the riverbank—natural ecosystems are well adapted to this ever-changing process. Pioneer vegetation thrives in these dynamic conditions, and young saplings are able to establish even on bare sandbars and gravel beds (bars).
In fact, the cyclical dance of erosion and sediment deposition is a vital creative force in shaping landscapes. It continually resets the natural habitat succession—from freshly formed point bars to meadows, then shrubs, young forests, and eventually mature woodlands. Each stage supports its own rich and unique set of flora and fauna.

Learn how natural river dynamic is a key to biodiversity
Understanding just how dynamic a river truly is reveals its role as a key driver of biodiversity. Without erosion, ecosystems would stagnate, leading only to the final stage—dense forest—which supports far less biodiversity. This is exactly what happens in heavily regulated rivers, where embankments, rip-raps, culverts, groynes, and other artificial structures halt the natural reshaping of the river corridor.
See a short video about the Drava River with strong erosion that creates extraordinary landscapes and biodiversity.